Our brains communicate with electrical and ava devine sex videoschemical signaling, but scientists have discovered that light stimulation could hold potential keys to manipulating neuronal communication pathways that influence motor control, sensory perception, memory, neurochemical production and mood – or cellular virtual reality, as a report from the Journal of Cell Biology describes it.
With the roll out of the White House's $300 million BRAIN Initiative in 2013, interest in uncovering the secrets of the human brain has accelerated and now includes many government agencies, public/private partnerships and universities.
Dating back to at least 1971, optogenetic research has matured enough to gain the attention of organizations such as the NIH, DARPA and IARPA, who are exploring the role that light-sensitive cells could soon play in fields surrounding neurobiological, including physical and mental health, human-machine interfacing, and advancing artificial intelligence through reverse brain engineering.
Current optogenetic experiments rely on extracting "opsins" (light-sensitive proteins) from plants which can be introduced to mammals by methods including injection and infection via adenovirus.
Once delivered into an organism, opsins can be expressed in eye, brain or skin cells, allowing their light-sensitivity to be remotely activated or silenced with timed pulses of light in different color wavelengths across the light spectrum that can target multiple bodily systems and cause a variety of biological effects.
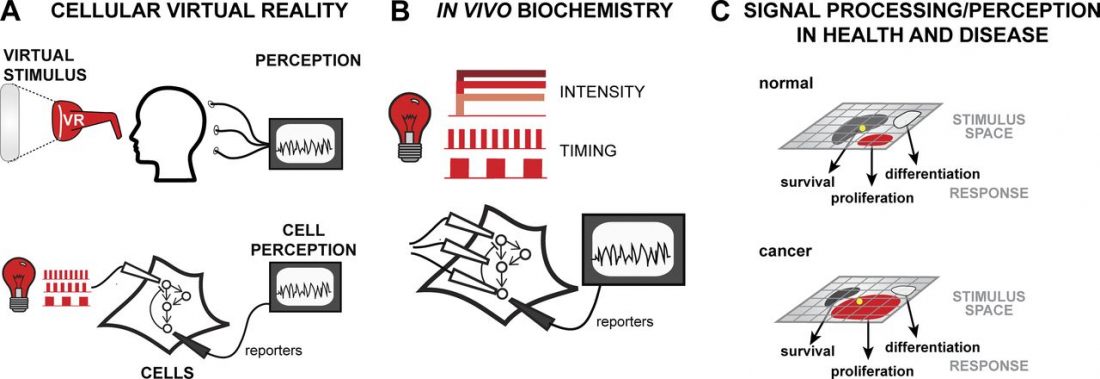
Researchers have suggested however that introducing opsins into an organism may not be a long-term requirement as methods are sought for using optogenetics on mammalian cells that respond naturally to light, such as those in the human retina.
As part of the BRAIN Initiative, scientists have been working on neuronal barcoding and completing a detailed online brain atlas for researchers. This is hoped to eventually provide a detailed circuit diagram of every neuron and synapse in the brain, which would allow various neuronal patterns to be identified so they can be triggered for the desired effect.
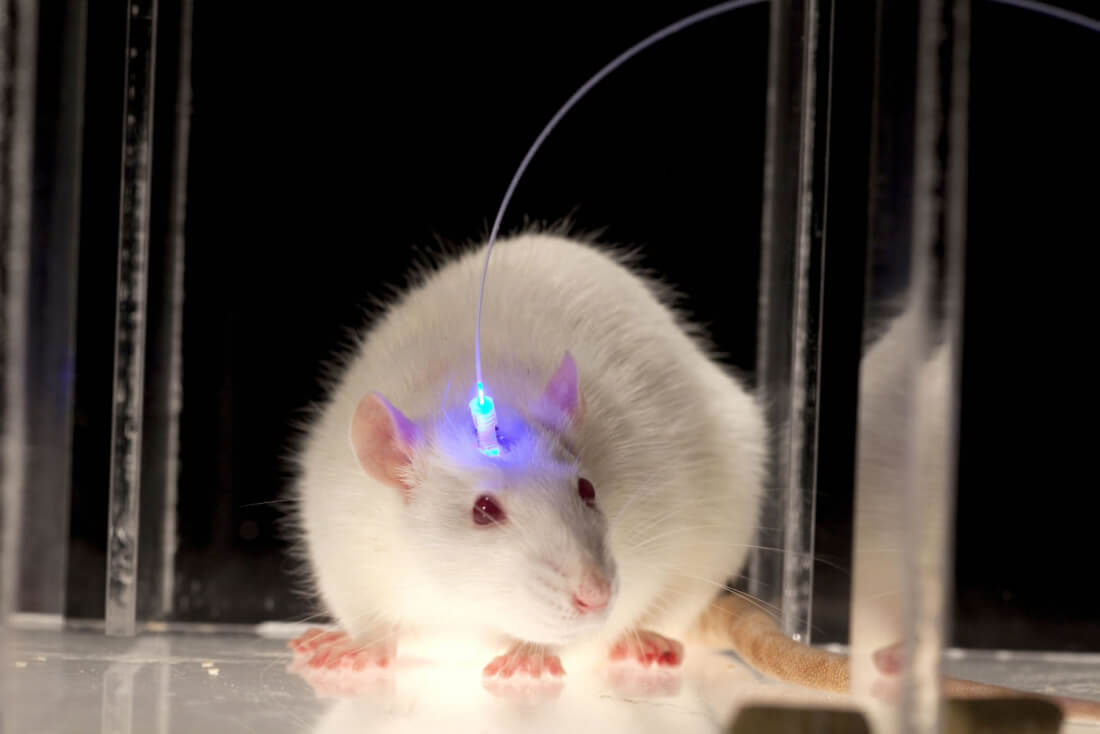
If targeted precisely enough with the appropriate light, it's thought that optogenetics could be used by manipulating neural circuits involved with pain, fear, reward, wakefulness and social behaviors. In one Yale study, for example, mice were infected with a virus which made their neurons sensitive to blue light. Scientists then used that light pathway to activate predatory behavior.
"...The researchers used a tiny optic fibre to shine a blue laser on the amygdala. This prompted the animals to tense their jaw and neck muscles... 'It's not just physiological, it's hunting, biting, releasing and eating. Those are motor sequences that require a lot of information...' [said an MIT neuroscientist]"
In 2015, optogenetics was combined with CRISPR to develop a set of photoactivatable tools that enable the editing of an organism's genome through the external use of light. Said tools can control the location, timing and reversibility of the genome editing process, whether that be activating, repressing or modifying a gene.
Optogenetics is also mentioned as an integral feature of the DARPA-funded Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program, a joint effort between six teams who are aiming to create an implantable neural interface over the next four years that is capable of high resolution brain-to-machine communication. Such advancements, for instance, could facilitate the development of mind-controlled prosthetics featuring touch sensation like the DARPA-backed 'Luke' arm (previously known as the 'Deka' arm).
In the past, DARPA has looked to optogenetic memory manipulation techniques for treating veterans with traumatic brain injury and/or PTSD through memory restoration or deletion.
More recently, during a November 2017 mental health conference with 30,000 attendees in Washington D.C., optogenetics was noted for the impact it's having on the ability to study the brain. According NPR science correspondent Jon Hamilton, the technology has allowed aspects of human mental health disorders to be reproduced in animals, aiding the mapping of neuronal circuits involved with issues such as depression.
Companies interested in the application of optogenetic technologies have begun emerging over the last decade, particularly since the FDA approved the technology in 2015 for use in treating an eye disorder known as "retinitis pigmentosa."
The approval prompted a clinical trial and optogenetic developments have since been used to restore partial vision in patients who were described as being "profoundly blind." Chronic pain management, epilepsy and Parkinson's are among many health issues that researchers are experimenting with addressing through optogenetics.
The technology is also contributing to other areas of research such as "sonogenetics," which uses low-pressure ultrasound to activate ultrasonically sensitized neurons. This is another area of interest for DARPA, which has funded Columbia University's endeavor to stimulate neurons using ultrasound and believes it could eventually lead to a magnetic version of the technology called "magnetogenetics."
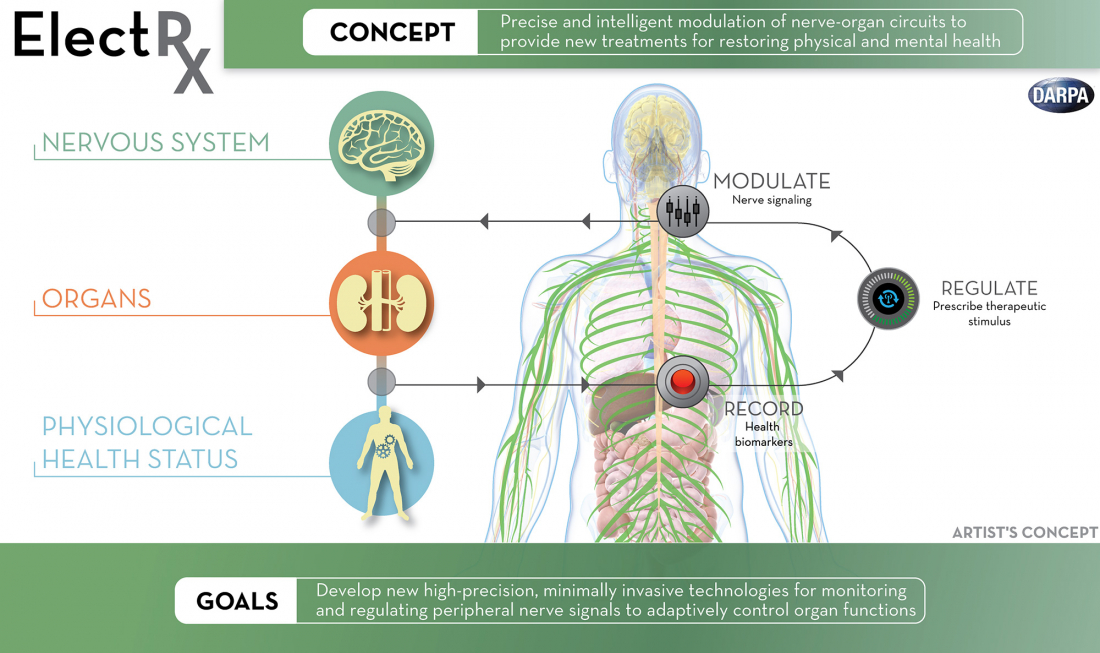
To investigate the therapeutic use of optogenetics, acoustics and electromagnetic fields, DARPA launched the ElectRX (Electrical Prescription) program in 2015, which is capable of stimulating, modulating and monitoring the body's peripheral nervous system. The research agency is also exploring how artificial intelligence could be used in closed-loop brain implants, such as the ability to detect patterns associated with mood disorders.
With enough progress, it's believed that optogenetics and its surrounding bodies of research may open the door to real-time brain mapping and biofeedback technologies, which could be used to treat all manner of ailments on the fly through closed-loop neuromodulation signals coming to and from an implanted device, ultimately eliminating the need for pharmaceuticals.
 Panthers vs. Falcons 2025 livestream: How to watch NFL online
Panthers vs. Falcons 2025 livestream: How to watch NFL online
 Wordle today: The answer and hints for May 9, 2025
Wordle today: The answer and hints for May 9, 2025
 NASA astronauts are proud bedwetters. They even practice.
NASA astronauts are proud bedwetters. They even practice.
 New Legion 9i gaming laptop: Lenovo unveils Legion 9i with glasses
New Legion 9i gaming laptop: Lenovo unveils Legion 9i with glasses
 The Year in Tech: 2014 Top Stories
The Year in Tech: 2014 Top Stories
 Best robot vacuum deal: Save $600 on Dreame X40 Ultra
Best robot vacuum deal: Save $600 on Dreame X40 Ultra
 Google Pixel Buds Pro 2: $40 off at Amazon
Google Pixel Buds Pro 2: $40 off at Amazon
 Meta's Threads is testing video ads
Meta's Threads is testing video ads
 Winter storm: See snow totals for Florida, Texas and other states online
Winter storm: See snow totals for Florida, Texas and other states online
 Lego's adorable Tiny Plants are on sale for $39.99
Lego's adorable Tiny Plants are on sale for $39.99
 Best Presidents' Day deal: Save $250 on Peloton Bike
Best Presidents' Day deal: Save $250 on Peloton Bike
 Fitbit Inspire 3: 20% off at Amazon
Fitbit Inspire 3: 20% off at Amazon
 MotoGP 2025 livestream: Watch France Grand Prix for free
MotoGP 2025 livestream: Watch France Grand Prix for free
 The USPS 'Informed Delivery' app is coming to iOS and Android
The USPS 'Informed Delivery' app is coming to iOS and Android
 Chiefs vs. Texans 2025 livestream: Watch NFL Playoffs for free
Chiefs vs. Texans 2025 livestream: Watch NFL Playoffs for free
 Best Fire TV Stick deal: Save $20 on 4K Max streaming stick
Best Fire TV Stick deal: Save $20 on 4K Max streaming stick
 NYT mini crossword answers for May 10, 2025
NYT mini crossword answers for May 10, 2025
 Best garmin deal: The Garmin Lily 2 Active is $50 off
Best garmin deal: The Garmin Lily 2 Active is $50 off
 CES 2025: Everything to expect
CES 2025: Everything to expect
 Best Apple M4 MacBook Pro deal: Lowest
Best Apple M4 MacBook Pro deal: Lowest
The future of retail is permanent popJeff Sessions trolled with KKK costume projected on a building in D.C.This watchmaker thinks this $200,000 Pokemon watch is the 'emblem of millennials'Jeff Sessions trolled with KKK costume projected on a building in D.C.Watch millions of people use Google's Quick, Draw in GIFsJustin Timberlake finally replies to that Seth Rogen tweetYouTube expands mobile livestreaming capabilities to more usersMiley Cyrus' Billboard performance made everyone with the last name Cyrus cryThursday may be a weather nerd's dream, but it's a nightmare for someCry of the Week: 'Shots Fired' finally gives us justice for Joey CampbellHow to share Google Photos animations to InstagramTwitter is incorrectly guessing the gender of trans users — and they aren't having itCan you find the hidden and scared government official?Inside the haunting, tooA new Sesame Place theme park is moving to the neighborhoodAlec Baldwin bid a poignant farewell to Trump on 'Saturday Night Live' finaleIn the U.S., trees are on the move because of climate changeWhy do 'The Bachelorette' producers hate Rachel Lindsay?Ted Cruz just made a really funny joke on Twitter, seriouslyPit bull on the brink of euthanasia gets second chance as a police dog instead Donald Trump now allegedly believes President Obama was born in America Amy Adams, smart script are key pieces of the engrossing puzzle that is 'Arrival' Taylor Swift sang along to a Calvin Harris track at Gigi Hadid's fashion show Shaq, Yao and Iverson: The 2016 Basketball Hall of Fame class makes me feel old Some police departments shelve body cameras, blame data costs Yahoo dishes the details behind its sale to Verizon in 360 GM recalls 4 million vehicles for airbag defect linked to death India to make rear sensors, speed warning system mandatory in cars Nissan's new Sentra SR Turbo is the sports sedan you can actually afford NFL players hold national anthem protests on opening Sunday No one has ever been as happy as this pug getting belly scratches Tailgating bro makes 'send beer money' sign, fellow sports fans do the rest Marine conservation efforts just took a major step forward Geoengineering is a bonkers plan, but it may be needed to tackle global warming Taylor Swift donates $5,000 to help fund a fan's funeral and medical expenses Greta Friedman, woman in iconic Times Square kiss photograph, dies at 92 Wikileaks retracts Twitter poll speculating about Clinton's health Donald Trump just gave an unexpected response to Hillary's pneumonia diagnosis Here's how the 'Epic Rap Battles' creators are gearing up for the Emmys Samsung Note7 owners told to stop using their phones and recall is imminent
1.8005s , 10543.734375 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【ava devine sex videos】,Warmth Information Network