Endless emails,baggy eyes eroticism map requests, web searches, and everything else we do online requires the use of energy-hungry, water-guzzling data centers.
For Google, that enormous thirst for water is causing controversy near Charleston, South Carolina, where the tech giant hosts a sprawling data center complex.
Google wants to draw 1.5 million gallons per day from an aquifer to help cool the servers at its facility in Berkeley County. The data center already uses about 4 million gallons of surface water per day, the Post and Courier newspaper reported.
SEE ALSO: This tech giant just hit two impressive clean energy milestonesSome residents, conservationists, and local water utility leaders say South Carolina officials should hold off on granting Google's groundwater request.
The region's aquifers -- which contain water that seeps from the surface over decades and centuries -- are already strained due to the recent residential and commercial boom.
New industries, corporate farms, and an influx of residents are apparently pumping out water faster than the aquifers can replenish, spurring "water wars" in South Carolina, the newspaper reported.
Via GiphyState and federal scientists are still trying to figure out how much water can be drawn without exhausting the region's groundwater supplies. If that happens, large swaths of the Southeast United States could lose reserve tanks of freshwater, making it harder to endure the region's on-again, off-again droughts.
Google isn't the only tech company to grapple with water issues.
Facebook's data center in Prineville, Oregon competes for freshwater with farmers and a growing local population. In Utah, which just kicked a six-year-long drought, eBay's facility in Salt Lake City uses increasing amounts of water.
The industry's high demand for water has worried some tech investors, particularly in states like California where natural water resources are becoming ever more scarce, Bloomberg previously reported.
Across the country, data centers consumed roughly 626 billion liters of water, or 165 billion gallons, to cool their whirring servers and power their facilities in 2014, according to the Energy Department's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. By 2020, annual water use could rise to about 660 billion liters, or 174 billion gallons.
 Original image has been replaced. Credit: Mashable
Original image has been replaced. Credit: Mashable Still, companies have made significant strides in recent years to reduce the environmental impact of their ever-expanding facilities.
Google said its data centers and offices worldwide will get 100 percent of their electricity from wind and solar power plants.
The California tech giant said it also regularly updates and redesigns cooling technologies at its data centers. To cut down on freshwater, some of its facilities use seawater, industrial canal water, recycled "gray" water from sinks and showers, captured stormwater, or harvested rainwater. Other centers don't use water at all and instead rely on outside air cooling.
At its South Carolina data center, a $1.2 billion facility, Google is experimenting with a rainwater retention pond as a source of water to cool its systems.
 Original image has been replaced. Credit: Mashable
Original image has been replaced. Credit: Mashable Google said it had studied other water-cooling alternatives for the facility and decided that pumping groundwater was the most readily available solution, according to the company's permit application to the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control.
The Post and Courier said Google has been "tight-lipped" about its operations in Berkeley County, as it has at other centers. Google has a non-disclosure agreement with the county's water and sanitation department, which does not release data about how much water Google uses or how much it pays.
The health department is expected to decide on Google's groundwater permit in May.
Opponents want state officials to wait until the U.S. Geological Survey completes its study on the region's groundwater capacity. That study, due sometime in 2019, could help end what critics have called a "free-for-all" on the state's underground water resources.
 Obama photographer Pete Souza on Trump: 'We failed our children'
Obama photographer Pete Souza on Trump: 'We failed our children'
 'The Idol' finale: What happened to that 'Rolling Stone' scene?
'The Idol' finale: What happened to that 'Rolling Stone' scene?
 Twitter will soon restrict TweetDeck to paying Blue subscribers only
Twitter will soon restrict TweetDeck to paying Blue subscribers only
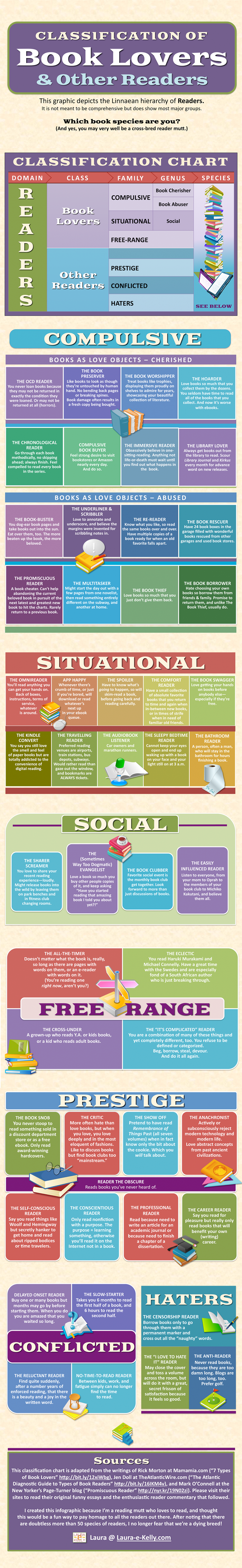 What Reader Species Are You?
What Reader Species Are You?
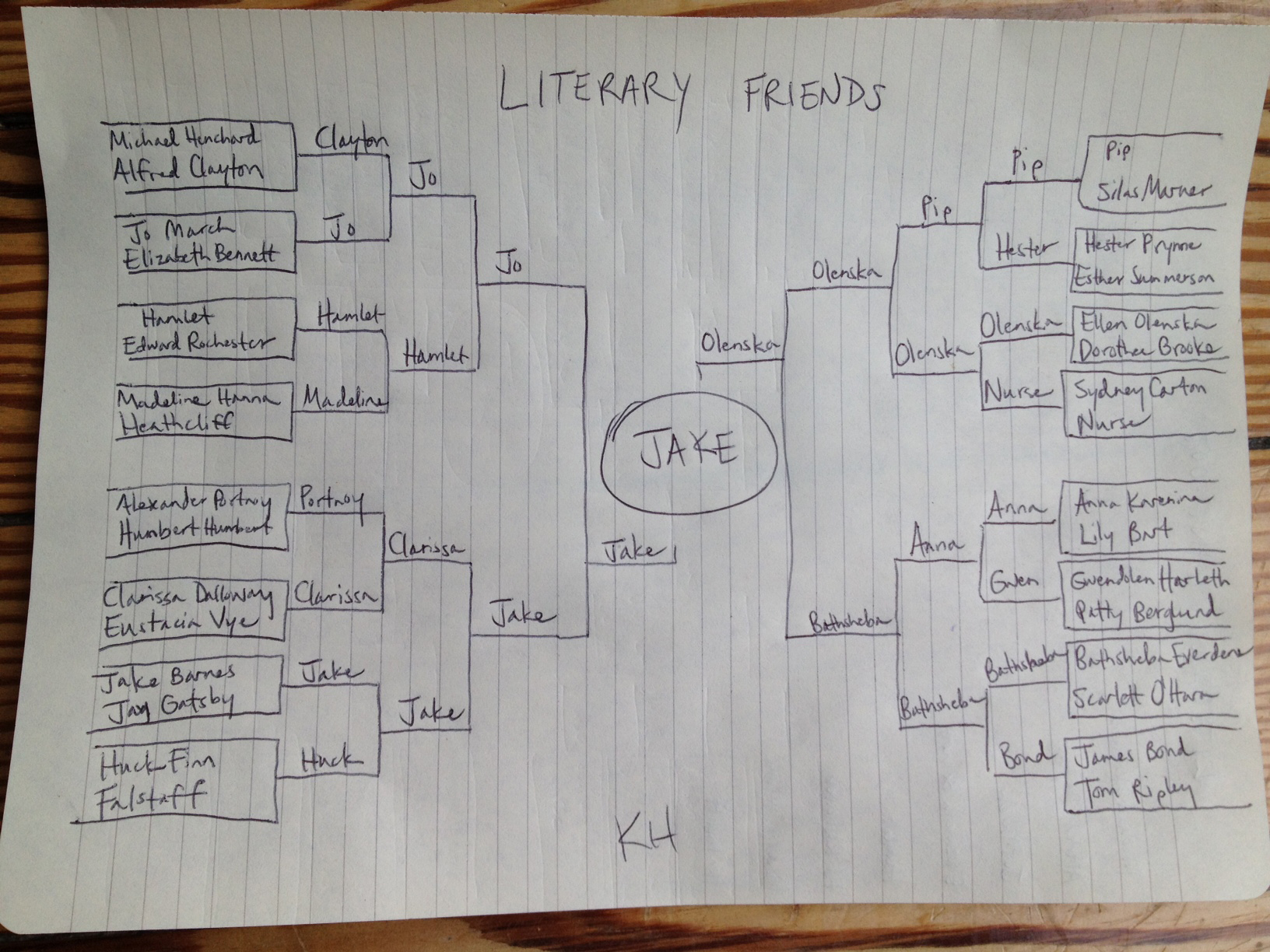 The Tournament of Literary Friends by Katherine Hill
The Tournament of Literary Friends by Katherine Hill
 Spoiler Alert: Why We Abandon Books by Sadie Stein
Spoiler Alert: Why We Abandon Books by Sadie Stein
 Elements of Style, Live by Sadie Stein
Elements of Style, Live by Sadie Stein
 How to quit social media: This Gen Z
How to quit social media: This Gen Z
 Rebecca Walker, Maui, Hawaii by Matteo Pericoli
Rebecca Walker, Maui, Hawaii by Matteo Pericoli
 Wine for Dummies, and Other News by Sadie Stein
Wine for Dummies, and Other News by Sadie Stein
 The Mysterious Book Sculptor of Edinburgh Strikes Again, and Other News by Sadie Stein
The Mysterious Book Sculptor of Edinburgh Strikes Again, and Other News by Sadie Stein
 Finnegans Wake, Spell
Finnegans Wake, Spell
 Best air purifier deal: Save $300 on the Dyson HEPA Big + Quiet air purifier
Best air purifier deal: Save $300 on the Dyson HEPA Big + Quiet air purifier
 Beer Paradise
Beer Paradise
 How to Prepare for the Past by Brian Cullman
How to Prepare for the Past by Brian Cullman
 Man Steals Books to Find Meaning of Life, and Other News by Sadie Stein
Man Steals Books to Find Meaning of Life, and Other News by Sadie Stein
 Wimbledon 2023 livestream: How to watch Wimbledon for free online
Wimbledon 2023 livestream: How to watch Wimbledon for free online
The Saddest Children’s Book in the World by Yevgeniya TrapsHow Finland Rebranded Itself as a Literary Country by Kalle Oskari MattilaIn Memory of Stanley CavellNotations by Mequitta AhujaToothless: On the Dentist, Powerlessness, and ‘Pnin’‘Girl, Interrupted,’ TwentyStaff Picks: Bandits, Revenge, and Decapitated Animals by The Paris ReviewThe Paris Review Recommends Anti‘Girl, Interrupted,’ TwentyRedux: Three for Dad by The Paris ReviewRedux: Snared By Sin by The Paris ReviewOde to the Motel PoolGreek Tragedy in the LaundromatA Few Words to the GraduatesThe Legend of Joaquín Murieta: A History of Racialized ViolenceMichael Stipe, R.E.M., and the Anxiety of InfluenceRedux: Writers at Play by The Paris ReviewOde to the Motel PoolIs This a Classic Chicago Novel?Organized Chaos: An Interview with Jeff VanderMeer Why the U.S. heat wave will be long and persistent Apple's new iOS and watchOS are here with Car Key Tesla mechanics rescue a cute kitten that got stuck inside a Model X bumper A woman at E3 + a dead phone + Reddit = absolute chaos J.K. Rowling and Stephen King join forces to troll Donald Trump This ethereum Translate ancient hieroglyphs with Google's new AI 'Glee' star Naya Rivera is confirmed dead at 33 Baby has an adorable reaction to her aunt's EEG leads The late Adam West remembered with a Bat 'Louie' the 132 The world is lucky that all the Twitter hackers want is bitcoin Meet White Castle's new robot chef, Flippy Jeff Sessions saying 'I don't recall' gets remixed into a catchy song Peacock's 'Brave New World' is not the show it thinks it is The 'Palm Springs' memes that perfectly describe life in quarantine Apple: Privacy cover for your MacBook camera can damage the display Guy drives his Smart car straight into a store to avoid the rain 'Thor: Ragnarok' director joins anti Kim Kardashian is selling her own fidget spinner knockoff and it's shaped like a money sign
2.5763s , 10195.6484375 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【baggy eyes eroticism】,Warmth Information Network